Fuses
A fuse is a short piece of metal, inserted in the circuit, which melts when excessive current flows through it and thus breaks the circuit.
The fuse element is generally made of materials (silver, copper etc.). It is inserted in series with the circuit to be protected. Under normal operating conditions the fuse element is at a temperature below its melting point. Therefore it carries the normal current without overheating. However when a short circuit or overload occurs through fuse increase beyond its rated value. This raises the temperature and fuse element melts, or disconnecting the circuit protected by it. In this way it protects the machines and equipment from damage due to excessive currents
 |
| A HRC fuse |
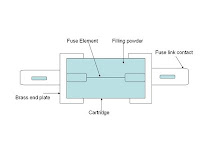 |
| Essential parts of a HRC fuse |
Desirable Characteristics of fuse element
The function of fuse elements is to carry the normal current without overheating but when the current exceed the normal value; it rapidly heats up to melting point and disconnects the circuit protected by it. In order that it may perform this function satisfactorily, the fuse element should have the following desirable characteristics.
- Low melting point such as tin, led
- High conductivity such as silver, copper
- Free form deterioration due to oxidation such as silver
- Low cost such as lead, tin, copper
Types of fuses
Fuse is the simplest current interrupting device for protection against excessive currents. Since the invention of first fuse by Edison; several improvements have been made and now a days, a variety of fuses are available. Some fuses also incorporate means for extinguishing the arc that appears when he fuses elements melts. In general fuses may be classified into
- Low voltage fuses
- High voltages fuses
Low voltage fuses
Low voltage fuses can be subdivided into two classes ie,
- Semi-closed rewireable fuse
- High rupturing capacity (H.R.C) cartridge fuse
The low-voltage fuses discussed so far have low normal current rating and breaking capacity. Therefore they cannot be successfully used on modern high voltage circuits. Intensive research by the manufacturers and supply engineers has led to the development of high voltage fuses. Some of the high voltage fuses are
- Cartridge type
- Liquid types
- Metal clad fuses
READ DETAILS