Air Compressor
Air Compressor used to compressed air for industrial or other different purpose.It is use to increase kinetic power of of air driven by electric motor or Diesel/ Gasoline engine by compressing and pressurizing air.
Classification of Compressor
Read about compressor classificarion
Air compressor can be classified in various.
The two main classification of Air Compressor are.
- Positive Displacement Type
- Dynamic Type
- Reciprocating Air Compressor.
- Rotary Air Compressor.
Rotary air compressor can be classified as
Different Parts
- Rotary Screw Compressor
- Rotary Vane compressor.
- Centrifugal Air Compressor
- Axial Flow Air Compressor
- Roots Blower Compressor.
- Low pressure Compressor(150 psi or less)
- Medium Pressure Compressor(151 psi to 1,000 ps)
- High pressure Compressor(about 1000 psi)
- Single stage
- Multi stage
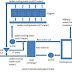
Different Parts
Different parts of air compressor are
- Air storage tank
- Air filter
- Inlet valve
- Exhaust valve
- Inlet port
- Exhaust port
- Piston
- Piston sleeve
- Connecting rod
- Eccentric bearing
- Discharge line
- Safety valve
- Motor housing
- Cooling fins or water cooling lining
Working principle
 |
| P-V diagram of a reciprocating compressor |
Compressor collect air through air filter then entered in the pressurizing chamber through inlet valve.Piston compressed the air and discharge take place through exhaust valves.Piston connected with crankshaft by connecting rod.A motor or diesel/gasoline engine drive the crank shaft.
The figure above shows P-V diagram of a single stage -single acting reciprocating compressor.
Process: a to1= Air is drawn into the cylinder on the suction stroke through air filter
Process: 1 to 2= The suction valve is closed and air is compressed according to the law Pvn = c
Process: 2 to b= The outler valve opens and air is delivered
Process: 1 to 2= The suction valve is closed and air is compressed according to the law Pvn = c
Process: 2 to b= The outler valve opens and air is delivered
Process: b to a= The delivery valve closes and the suction valve opens
Capacity and Efficiency of Compressor
The capacity of an air compressor is measured by the amount of free air (at sea level) that it can compress to a specified pressure(usually 100 psi/min) under the conditions of 68°F and a relative humidity of 38 percent. This capacity is expressed in cubic feet per minute (cfm)
Efficiency of a compressor is define by the equation
Where,
P(out) = utput pressure of compressed air
P(in) = Inlet pressure of sucked air
T(in) = Inlet temperature of sucked air
T(out) = Outlet temperature of compressed air
Capacity and Efficiency of Compressor
The capacity of an air compressor is measured by the amount of free air (at sea level) that it can compress to a specified pressure(usually 100 psi/min) under the conditions of 68°F and a relative humidity of 38 percent. This capacity is expressed in cubic feet per minute (cfm)
Efficiency of a compressor is define by the equation
Where,
P(out) = utput pressure of compressed air
P(in) = Inlet pressure of sucked air
T(in) = Inlet temperature of sucked air
T(out) = Outlet temperature of compressed air