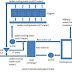
Reciprocating Pump
Reciprocating pump runs by the principle of pushing the liquid by a plunger,piston or bucket that executes a reciprocating motion through a cylinder.
Main Components
Main component of a reciprocating pump are
- Piston or Plunger or Bucket
- Suction line
- Delivery line
- Suction valve
- Delivery line
- Crank and connecting rod
- Liquid container or cylinder
- Packing (used as liquid seal)
- Casing of crankcase
- Bearing for crankshaft and connection rod
- Reduction gear
Working Principle
Through the suction line liquid is filled to the cylinder through suction check valve.Then the piston connected with crankshaft through connection rod push the liquid and the liquid is discharge through delivery line.Electric motor usually used power up the crankshaft.Rotary motion convert into reciprocating motion.When piston moves from bdc to tdc it creates a vacuum which helps to suck liquid to the cylinder.
Discharge and Efficiency calculation
Discharge of a reciprocating pump is calculated by the following equation
Q=(ALN)/60
Where,
Q= Discharge in m3/s
A= Cross section area of piston or cylinder in m2
L= Stroke length in m
N= Speed of the crankshaft in R.P.M
The efficiency of reciprocating pump is calculated by the following equation
Efficiency= P(out) / P(in)
Advantages of using Reciprocating Pump
Following are the advantages of using reciprocation pump
- High efficiency
- It can produce high pressure
- Change in pressure does not affect the flow rate
- Have a function of self priming
Disadvantages
- It provide a pulsating flow
- For high viscous fluid suction stroke is difficult
- Gives low volume rate of flow
- Cost is high
- Maintenance process is difficult due to close fitting moving parts